Bleeding Gums and Periodontal Disease

For many people, the first symptom of gum disease to appear is bleeding gums. If your gums are inflamed or bleeding, it may be an indication that you have periodontal disease, also known as gum disease or gum infection. This condition occurs when bacteria irritate the soft tissue supporting your teeth, causing your gums to become red and swollen and your teeth to loosen. Gingivitis can lead to more severe forms of periodontal disease, including bone loss around the teeth and eventually tooth loss.
What are the Causes of Gums Bleeding When I Wake Up?
Bleeding gums can be a common indicator of periodontal disease, which is a condition that attacks gum tissue. If you’re suffering from bleeding around your gums or have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, there are treatments available to help improve your situation. While it may seem like nothing more than annoying bleeding in your mouth, keep in mind that it can become much more serious without treatment. If you suspect bleeding gums are due to other causes unrelated to periodontal disease, talk with your dentist for advice on what steps might be best for your situation, including appropriate bleeding gums treatment.
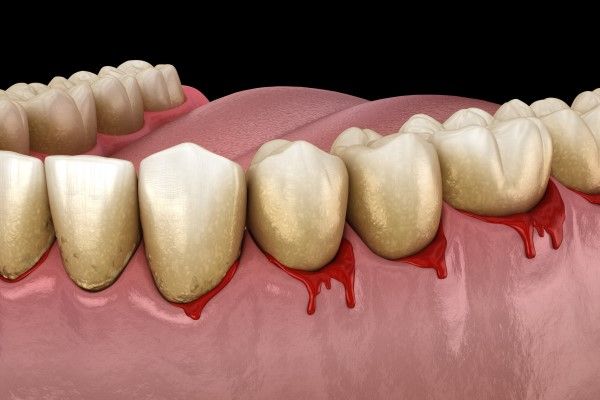
Understanding Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums, also known as gum bleeding, is a common symptom that can be caused by various factors, including medical conditions, dental diseases, and poor oral hygiene. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of bleeding gums to determine the appropriate treatment. Bleeding gums can be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires immediate attention. In some cases, bleeding gums can be a warning sign of severe gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
Medical Conditions that Cause Bleeding
Certain medical conditions can cause bleeding gums, including diabetes, leukemia, and gum cancer. Diabetes can make it harder for the body to heal, making gum disease worse. Leukemia can cause a low platelet count, making it harder to stop bleeding in the gums. Gum cancer can cause bleeding gums due to the growth of abnormal cells. Other medical conditions, such as HIV infection, anemia, and thrombocytopenia, can also cause bleeding gums.
Hormonal Changes and Bleeding
Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can cause gum problems, including bleeding gums. Hormonal fluctuations can lead to inflammation and sore gums, making them more susceptible to bleeding. Good oral hygiene practices can help prevent bleeding gums during these times. Regular dental check-ups can also help detect any underlying gum disease.
Stress and Bleeding
Stress can cause bleeding gums due to inflammation and immunosuppression. Stress can induce an immunosuppressed state, encouraging bacterial infection and inhibiting normal coagulation processes. Stress can also cause gingival inflammation, making the gums more susceptible to trauma. Practicing good oral hygiene and managing stress through relaxation techniques can help prevent bleeding gums.
Medications and Substances that Increase Bleeding Risk
Certain medications and substances can increase the risk of bleeding gums, including anticoagulants, aspirin, and ibuprofen. These medications can thin the blood, making it harder to stop bleeding in the gums. Smoking and tobacco products can also cause gum disease and bleeding gums. Avoiding these substances and practicing good oral hygiene can help prevent bleeding gums.
How Can I Stop My Gums From Bleeding Due to Gum Disease?
It may be a symptom of a more severe problem, but it’s still not a good thing. If you notice your gums bleeding when you brush or floss, it could be a sign that you’re at risk for periodontal disease. Here are some symptoms to watch out for: red, swollen gums; bleeding while brushing or flossing; receding gum line; soreness in teeth or around teeth after eating hot/cold foods. And if you notice any of these symptoms, make an appointment with your dentist right away and ensure you are practicing proper oral hygiene.
Even if you aren’t currently experiencing any gum bleeding, it can be helpful to know what to do if your gums start to bleed again. First, continue flossing gently so as not to irritate the gums. If you are taking blood thinning over the counter pain relievers like ibuprofen, aspirin or naproxen consider stopping this and see if it helps your gum bleeding.
How Do I Prevent Bleeding Gums?
If you’re experiencing bleeding, there are a few things you can do to try to prevent it. The most important thing is to take care of your teeth and brush your teeth daily. This will not only help avoid bleeding but also reduce your risk of tooth decay, gum infection, or tooth loss. It is recommended to brush at least twice per day, once in the morning after you wake up and again before bedtime at night.
You should also be sure to floss your teeth daily, as well. Flossing helps to reduce plaque and tartar build-up on your teeth, leading to gum disease and bleeding. It’s generally recommended that you floss once a day at night before bed but doing it more than once per day if possible is also helpful. Consider using an antibacterial/antimicrobial mouthwash. Common ingredients that can help with bleeding are cetylpyridinium chloride, certain essential oils, and stannous fluoride. Flouride containing mouthwashes also help to strengthen the enamel.
If you’re having trouble finding time to fit these activities into your schedule, try using a timer set up to remind you each day of when it’s time for your next dental care ritual.